In today’s fast-paced world, various businesses are going global. To ensure smooth and secure cross-border transactions, exporters rely on SWIFT transfers. SWIFT transfer plays a crucial role in helping Indian businesses receive international payments efficiently and reliably.
If you’re new to the export world, you must understand the process of the SWIFT network, how it works, the step-by-step process, the charges related to it, and the better alternative. Whether you’re new to the domain or are experienced, you need to choose a platform that can help in a quicker, affordable, and hassle-free, cross-border transaction platform.
This guide will not only help you understand SWIFT codes, the SWIFT transfer process, and how to track them, but also other alternatives that can help you streamline the global transactions of your business.
What is SWIFT?
SWIFT or Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication is a message network used by financial institutions such as banks to transfer money globally. Financial organizations can use it to securely communicate with each other using predefined messages and instructions. As part of their global trade activities, exporters use SWIFT to transfer international money from one bank account to another.
In simpler words, a SWIFT payment allows international electronic transactions through an intermediary bank. The SWIFT network itself neither transfers funds nor is a banking system. However, it connects banks around the world using SWIFT codes. The SWIFT payment network allows businessmen and freelancers to send or receive international money via credit card payments as well.
As of 2024, SWIFT connects over 11,000 financial institutions in 210 countries and territories. This global network facilitates millions of transactions daily, exceeding $150 trillion annually.
Understanding SWIFT code
Using SWIFT means that you’re not sending a ‘money transfer’, instead, you’re creating a ‘payment order’ between two banks. Communication between these two banks is made via SWIFT code.
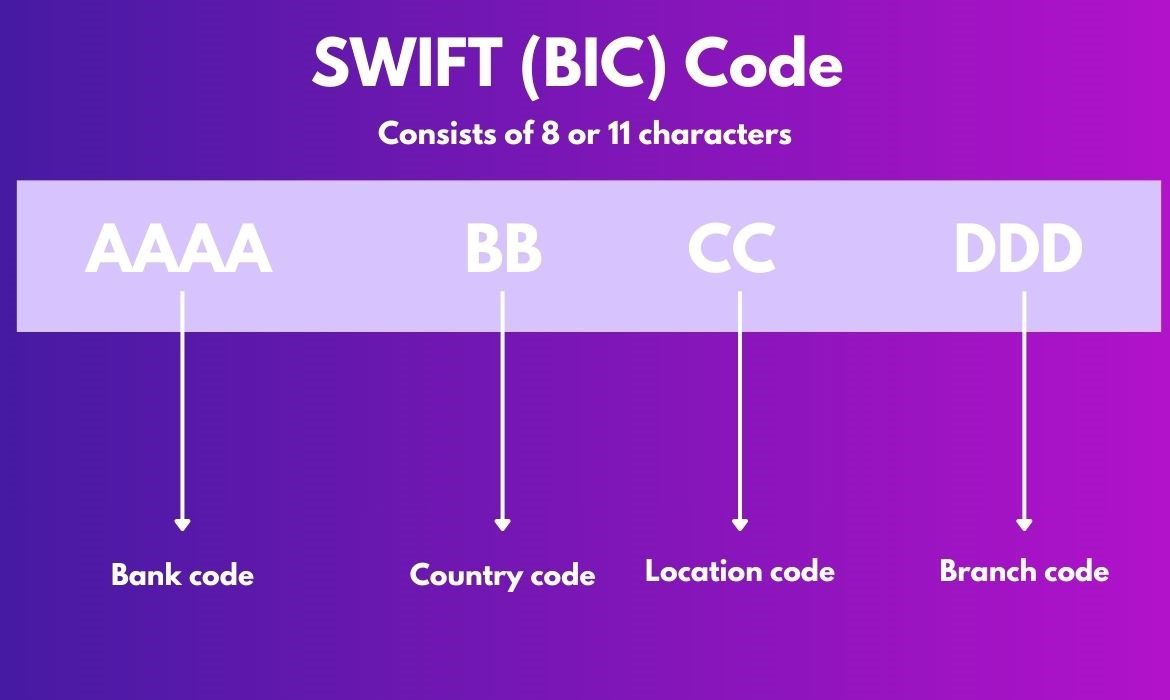
SWIFT uses unique codes for its member organizations to help them identify all parties in a transaction. These codes are typically 8 or 11 characters long and contain key details about the banks involved – whether they’re sending, receiving, or acting as intermediaries.
Let’s break down what a SWIFT code looks like:
- Bank Code (4 letters): The first four characters represent the specific bank or institution. For example, ‘UBIN’ for Union Bank of India, or ‘DUET’ for Duetsche Bank.
- Country Code (2 letters): The next two characters indicate the country where the bank is located. For example, ‘US’ for the United States or ‘IN’ for India.
- Location Code (2 letters or digits): This portion specifies the bank’s location within the country, helping to pinpoint the city or region. For example, ‘BB’ is for Mumbai and ‘DE’ is for New Delhi.
- Branch Code (3 letters or digits): This part directs the transaction to the correct branch of the bank. Not all SWIFT codes include a branch code, which is why some are only 8 characters long.
SWIFT code examples
Here are some SWIFT code examples with their breakdown-
- IDFBINBBMUM: This code is for IDFC bank’s Mumbai branch. Here ‘IDFB’ is the bank code, ‘IN’ is for India, ‘BB’ stands for Mumbai, and ‘MUM’ represents the bank’s branch.
- BARCGB22: This code is for Barclays Bank Plc. ‘BARC’ indicates the bank code, ‘GB’ represents the country code which is ‘UK’ in this case, and ‘22’ indicates the branch code.
How to initiate a SWIFT transfer?
For a SWIFT transfer to be carried out successfully, there are six parties involved. Let’s take a look at them first.
- Sender: An individual or business initiating the transfer.
- Sender’s bank: The bank who is sending the fund from the sender’s behalf.
- SWIFT network: The secure messaging system that shares payment instructions.
- Intermediary banks: When the sender and recipient’s banks do not have a direct relationship, these banks facilitate transfers.
- Recipient’s bank: The bank where the funds are ultimately credited.
- Recipient: The individual or business receiving the funds.
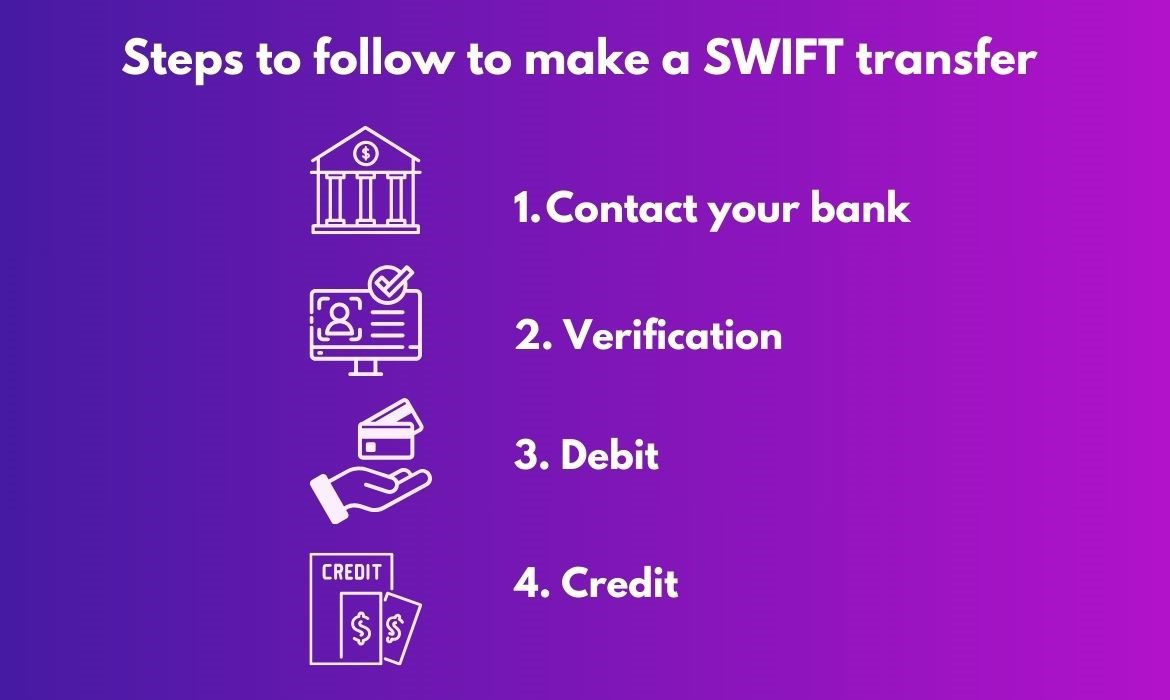
Steps to follow to make a SWIFT transfer
There are four steps involved in making a SWIFT Transfer from one bank to another and they are-
- Contact your bank: You can initiate SWIFT transfer either by visiting the bank or by logging into the bank’s online portal. You will require to fill in certain details such as recipient’s name, their bank name, address, SWIFT/ BIC code, currency, and the transfer amount.
- Verification: Your bank will need to verify all the details filled in by you and ensure that you’ve enough amount in your account for the transfer.
- Debit: Following the verification, your bank will deduct the amount from your account. You will receive a confirmation message or reference number once the amount is deducted.
- Credit: Using the SWIFT network, the funds will be transferred to the recipient’s bank. Now the recipient’s bank will confirm the transaction details and credit the amount to their account.
When the sender’s and the receiver’s bank do not have a direct relationship, an intermediary bank gets involved. Therefore, also ensure that you provide proper information about the intermediary bank used.
How long does the SWIFT transfer take?
While most transactions can be finalized within one day, SWIFT transfers can take anywhere between 1 to 5 working days. However, there can be delays in the transfer due to-
- National or bank holiday.
- The involvement of intermediary bank.
- Incorrect information about the intermediary or recipient’s bank.
- Variations in banking infrastructure and processing times.
- Technical errors or system outages.
Can you track the SWIFT transfer?
Yes, once the SWIFT transfer is initiated, you can track the progress in two ways:
- SWIFT payment reference number: Once the amount is debited from your account, you will receive a reference number. Using this reference number and the bank’s assistance, you will be able to check the status of the transfer.
- SWIFT tracking tool: You can also use the tracking tool on SWIFT’s official website to check the live status of your payment.
The types of fees involved in a SWIFT transfer
There are various charges or fees involved in SWIFT transfer and let us take a look at those-
- Wire fee: This fee ranges anywhere between $30 to $150 and is charged by the sender’s bank for processing the international transfer.
- Foreign Inward Remittance Advice (FIRA) fee: This document acknowledges receipt of funds, which can cost from $5 to $50 in India.
- Foreign Exchange (Forex or FX) fee: It is the difference between the interbank exchange rate and the rate offered to the customer. For INR/ USD, this fee is generally Rs. 0.90/USD.
- Transaction fee: The bank charges a transaction fee of $5 to $50 to process the international transfer.
- Double currency conversion rate: There is a possibility that banks will impose double conversion charges, typically 3%-5% of the exchange rate, when the sending bank account currency differs from the transfer currency.
Tips for streamlining SWIFT transactions
The two most important tips that will help you streamline your SWIFT transactions are-
- Selecting the right bank: Make sure your bank has a strong relationship with global institutions so that you can conduct seamless international transfers. Also, consider cross-border fintech platforms like BRISKPE that offer competitive fees.
- Prepare proper documentation: Keep up to date Know Your Customer (KYC) documents, including identity verification and legal entity information. It is important to gather all recipient details, such as their full name, address, bank name, SWIFT code, and account number, in order to streamline the transaction process.
What’s the alternative to SWIFT transfer?
Indian goods and service exporters have a few different SWIFT alternatives. The two most commonly used payment services are credit cards and PayPal. While credit card transactions are quick, they have high transaction fees (~2 to 4%) and have around 20% failure rate.
PayPal is another convenient alternative but can charge up to 6 to 8% in fees, reducing the earnings of freelancers and business owners. However, platforms like BRISKPE use virtual accounts to receive payments internationally. With our web portal and mobile application, exporters can receive payments within 24 hours. Moreover, we charge only 1% transaction fees (incl. GST), that makes us a better alternative than most platforms.
Conclusion
SWIFT network plays an important role in transferring funds across borders. The article covers all the necessary details you require to smoothly process your cross-border transaction. Although, you need to make sure that you have all the correct details about the recipient. Moreover, stay aware of the fees charged by the banks, and the best practices to ensure efficient transactions. With the right approach and fintech companies can BRISKPE, exporters can receive global payments easily and in a hassle-free manner.